GEMM
coalesced
__global__ void gemm(float *A, float *B, float *C, unsigned int N) {
unsigned int row = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
unsigned int col = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
float sum = 0.0f;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
sum += A[row * N + i] + B[col + N * i];
}
C[row*N + col] = sum;
}tiled gemm
Example:
- 4 tiles
C = A · BC[0][0] = A[0][0] · B[0][0] + A[0][1] · B[1][0](A[0][0], B[0][0])and(A[0][1], B[1][0])are shared by the same thread block to decrease global memory read.
__global__ void tiled_gemm(float *A, float *B, float *C, unsigned int N) {
__shared__ float A_s[TILE_DIM][TILE_DIM];
__shared__ float B_s[TILE_DIM][TILE_DIM];
unsigned int row = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
unsigned int col = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
float sum = 0.0f;
for (unsigned int t = 0; t < N / TILE_DIM; ++t) {
// Load tile to shared memory
A_s[threadIdx.y][threadIdx.x] = A[row * N + t * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.x];
B_s[threadIdx.y][threadIdx.x] = B[col + (t * TILE_DIM + threadIdx.y) * N];
__syncthreads(); // wait for others to finish before computing
// Compute with tile
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < TILE_DIM; ++i) {
sum += A_s[threadIdx.y][i] * B_s[i][threadIdx.x];
}
__syncthreads(); // wait for others to finish computing before loading
}
C[row * N + col] = sum;
}Reduction
naive
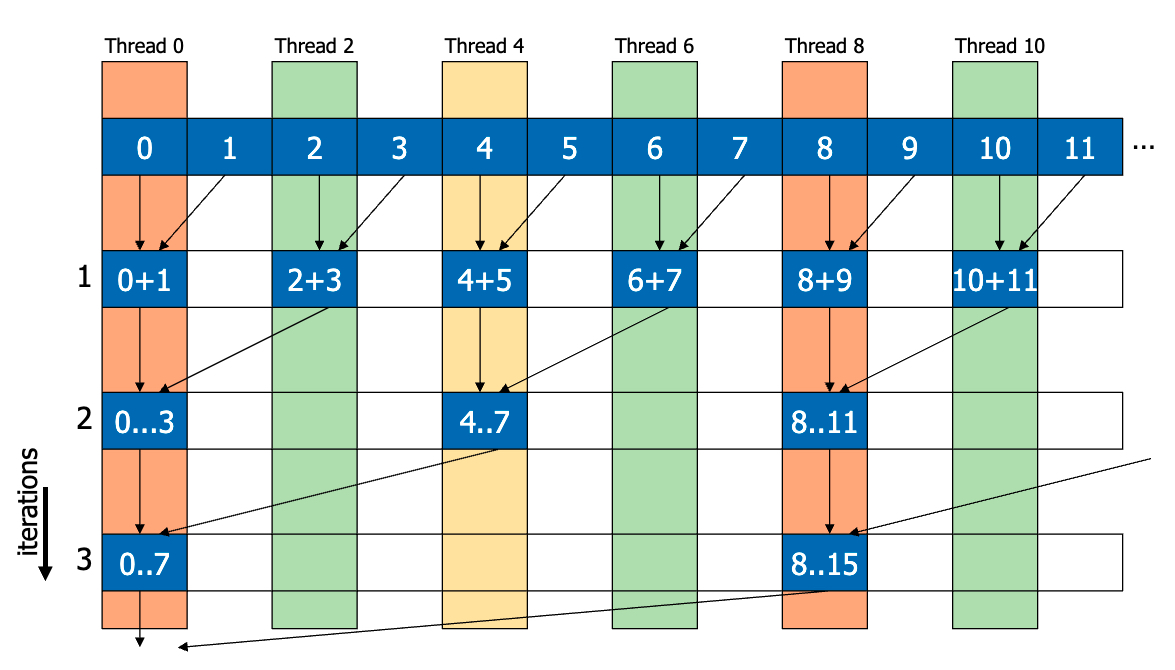
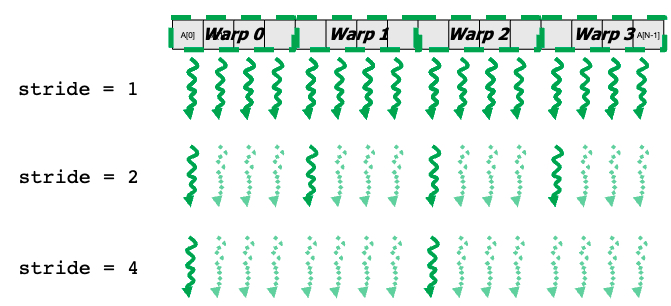
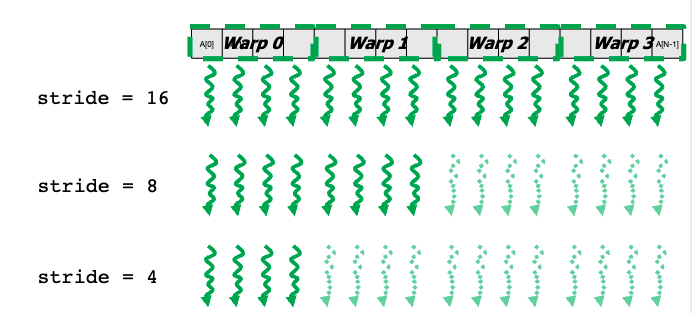
__shared__ float partialSums[];
unsigned int t = threadIdx.x;
for (int stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x / 2; stride *= 2) {
if (t % (2 * stride) == 0) {
partialSums[t] += partialSums[t + stride];
}
}divergence free
__shared__ float partialSums[];
unsigned int t = threadIdx.x;
for (int stride = blockDim.x; stride > 0; stride >> 1) {
__syncthreads();
if (t < stride) {
partialSums[t] = partialSums
}
}warp shuffle
- 每个线程块首先在共享内存中执行归约操作。通过这种方式,线程块内的线程可以快速地累加数据
- 当归约达到 WARP_SIZE 或更少的元素时,算法切换到使用 CUDA 的 shuffle 指令进行 warp 级别的归约。 CUDA 的 shuffle 指令允许在一个 warp内的线程之间直接交换数据,而无需通过共享内存进行同步。这大大提高了归约的效率。
__global__ void reduce_kernel(int *input, int *partialSums, unsigned int N) {
// Load data into shared memory
...
// Reduction tree in shared memory
for(unsigned int stride = BLOCK_DIM/2; stride > WARP_SIZE; stride /= 2) {
if(threadIdx.x < stride) {
input_s[threadIdx.x] += input_s[threadIdx.x + stride];
}
__syncthreads();
}
// Reduction tree with shuffle instructions
float sum;
if(threadIdx.x < WARP_SIZE) {
sum = input_s[threadIdx.x] + input_s[threadIdx.x + WARP_SIZE];
for(unsigned int stride = WARP_SIZE/2; stride > 0; stride /= 2) {
sum += __shfl_down_sync(0xffffffff, sum, stride);
}
}
// Store partial sum
if(threadIdx.x == 0) {
partialSums[blockIdx.x] = sum;
}
}thread coarsensing
__global__ void reduce_kernel(int *input, int *partialSums, unsigned int N) {
__shared__ int input_s[BLOCK_SIZE];
unsigned int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; // global thread index
const unsigned int gridSize = gridDim.x * blockDim.x; // total number of threads
int muSum = 0; // Local (per-thread) sum
while (i < N) {
mySum += input[i];
i += gridSize;
}
input_s[threadIdx.x] = mySum;
...
}Histogram
sequential
void histogram_calc(unsigned int *histo,
unsigned int *input,
unsigned int input_size) {
int i = 0;
while (i < input_size) {
unsigned int val = input[i];
histo[val] += 1;
i++;
}
}simple
__gloabl__ void histogram_calc(unsigned int *histo,
unsigned int *input,
unsigned int input_size) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int stride = blockDim.x * gridDim.x;
while (i < input_size) {
unsigned int val = input[i];
atomicAdd(&histo[val], 1);
i += stride;
}
}Privatization + Coarsening
Privatization is an optimization technique where multiple private copies of an output are maintained, then the global copy is updated on completion
- Reduce contention on global memory
- If the output is small enough, the private copy can be placed in shared memory reducing access latnecy.
Coarsening: Each block processes several chunks.
__global__ void histogram_kernel(unsigned int *histo, unsigned int *input, unsigned int input_size){
int tid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; // Thread index
int stride = blockDim.x * gridDim.x; // Total number of threads
__shared__ unsigned int histo_s[BINS]; // Private per-block sub-histogram
// Sub-histogram initialization
for(int i = threadIdx.x; i < BINS; i += blockDim.x) {
histo_s[i] = 0;
}
__syncthreads(); // Intra-block synchronization
// Main loop to compute per-block sub-histograms
for(int i = tid; i < input_size ; i += stride) {
unsigned int val = input[i]; // Global memory read (coalesced)
atomicAdd(&histo_s[val], 1); // Atomic addition in shared memory
}
__syncthreads(); // Intra-block synchronization
// Merge per-block sub-histograms and write to global memory
for(int i = threadIdx.x; i < BINS; i += blockDim.x) {
// Atomic addition in global memory
atomicAdd(histo + i, histo_s[i]);
}
}convolution
Convolution applies a filter or mask or kernel* on eachelement of the input (e.g., a signal, an image, a frame) toobtain a new value, which is a weighted sum of a set ofneighboring input elements
- convolutions are traditionally used for feature
detection in image processing
- They can be used as neural network layers
- convolutions have an advantage over fully connected
layers (e.g. in MLP)
- loacl weights: They compute on only a window around the element of interest
- data sharing via on-chip memories is feasible
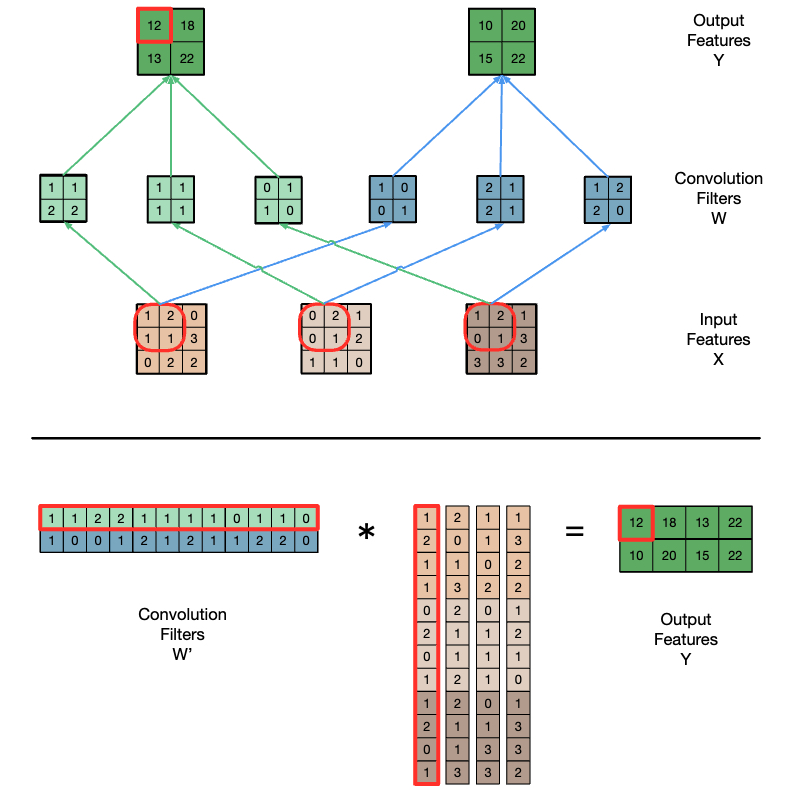
simple
__global__ void convolution_1D_basic_kernel(float *N, float *M, float *P,
int Mask_Width, int Width) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; // Index of output element
float Pvalue = 0;
int N_start_point = i - (Mask_Width/2); // Index of first neighbor
for (int j = 0; j < Mask_Width; j++) {
// Check the boundaries
if (N_start_point + j >= 0 && N_start_point + j < Width) {
Pvalue += N[N_start_point + j] * M[j]; // Multiply and accumulate
}
}
P[i] = Pvalue; // Store output element
}