Exploiting scale in both training data and model size has been central to the success of deep learning. When datasets are sufficiently large, increasing the capacity (number of parameters) of neural networks can give much better prediction accuracy.
Idea
The basic idea of MoE is split the FFN into multiple sub-networks(experts), for each input token, only part of sub-networks(experts) are activated. Different sub-networks behavior as different “experts”, during training they absorb different information and knowledge from the dataset, during inferencing only part of experts are activated based on the input token.
- Gating Network: This small neural network takes the input and learns to determine which experts are most relevant for processing that specific input. It produces scores or probabilities for each expert
Dense/Sparse Layer
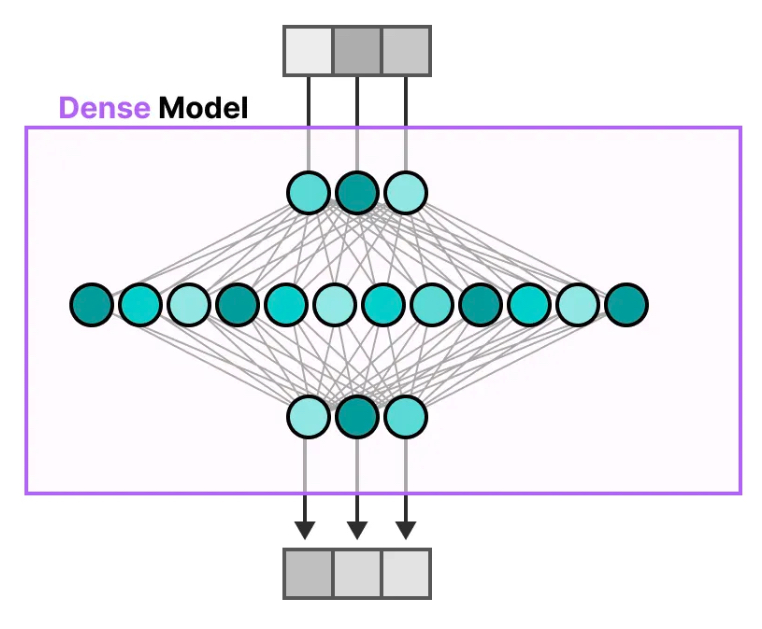
Dense Layer
FFNN (Feedforward Neural Network)
An FFNN allows the model to use the contextual information created by the attention mechanism, transforming it further to capture more complex relationships in the data.
MLP is a type of FFNN
Sparse Layer
Only activate a portion of the parameters
Each expert learns different information during training
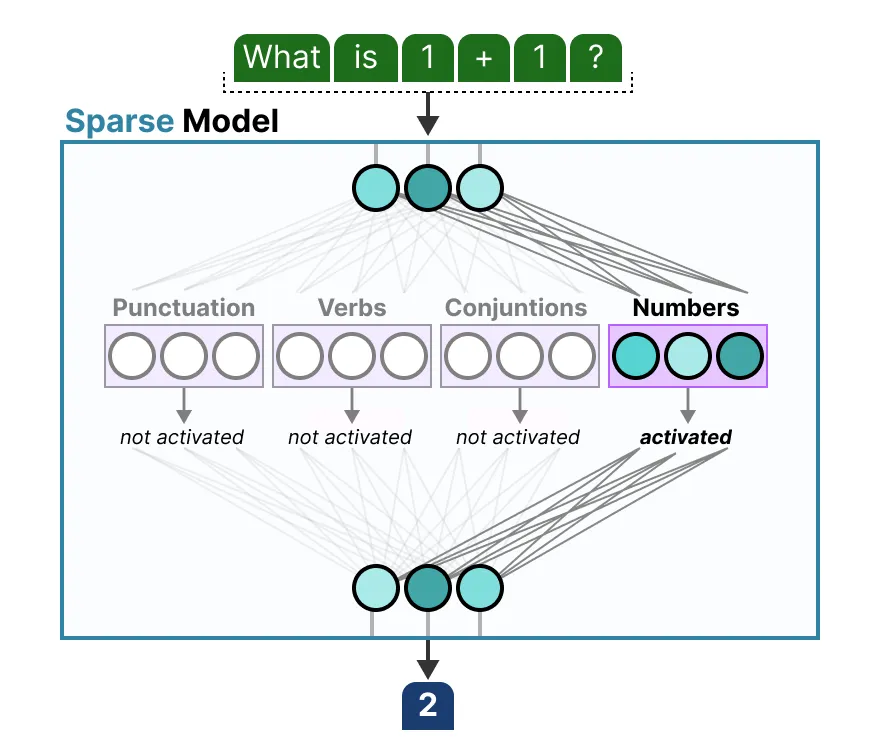
Expert
MoEGate:选择专家的模块,为一个 token
选择专家,输入是 embedding + attention。
一个标准的 transformer block:
x ──▶ LayerNorm
└──▶ Multi-Head Attention ───▶ residual add
↓
[hidden_state]
↓
LayerNorm
↓
FeedForward(原版)
↓
MoE(替代版)
↓
residual add
↓
output x# Before MoE
# MoE input = Attention Output + Residual = hidden_state
hidden_state = x + MultiHeadAttention(LayerNorm(x))
# Use MoE to replace FFN
output = FFN(LayerNorm(hidden_state))
output = MoE(LayerNorm(hidden_state))首先通过 MoEGate 计算所有 token 的 logits,计算完之后通过 grouped_topk 为每一个 token 选择若干专家。
- 在 deepseek v3 中,从 256 个专家中选择 8 个
Routing Function
Three general ideas:
- token choose experts
- expert choose tokens
- globally decide expert assignments
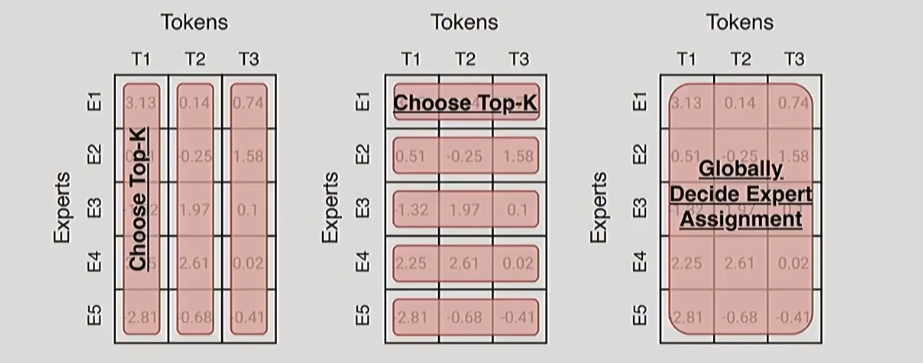
In practice, almost all the MoEs do token chooses top k. So each token is going to rank order experts by affinity(计算每个专家的亲和度,这也是 MoEGate 做的事情),and then there’s going to be top K choice.
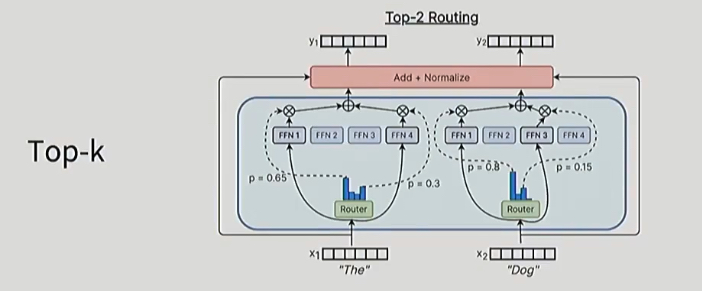
\[ \mathbf{h}_t^l = \sum_{i=1}^{N} \left( g_{i,t} \, \mathrm{FFN}_i\left( \mathbf{u}_t^l \right) \right) + \mathbf{u}_t^l, \]
\[ g_{i,t} = \begin{cases} s_{i,t}, & \text{if } s_{i,t} \in \mathrm{Topk}\left(\{s_{j,t} \mid 1 \leq j \leq N\}, K \right), \\ 0, & \text{otherwise}, \end{cases} \]
\[ s_{i,t} = \mathrm{Softmax}_i\left( \left( \mathbf{u}_t^l \right)^\top \mathbf{e}_i^l \right) \]
Fine Grained Expert
标准 MoE
标准 MoE 做 token level routing
- 输入 token 的完整 hidden vector(例如 4096 维)会被送到 1 或几个专家。
- 举例:一个 token 可能被分配到专家 3 和专家 7,这两个专家分别处理整个 hidden vector。
Fine-Grained Expert
Fined Grained MoE 做维度级的 routing
将每个 token 的 hidden vector 拆成多个 chunk(段),例如将 4096 拆成 4 个 1024 维小段。
然后为每段单独选择专家:
- 第一个 chunk → 专家 1
- 第二个 chunk → 专家 5
- 第三个 chunk → 专家 1
- 第四个 chunk → 专家 3
类似于专家是在维度上并行拼接,而不是处理整个 token。
Practice
deepseek 之前大多数 MoE 时间都是选取 8-16 个专家,然后在 forward 的过程中激活其中两个专家,deepseek v3 做了一个非常激进的配置,在 256 专家中激活 8 个专家。
| Model | Routed | Active | Shared | Fine-grained ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GShard | 2048 | 2 | 0 | |
| Switch Transformer | 64 | 1 | 0 | |
| ST-MOE | 64 | 2 | 0 | |
| Mixtral | 8 | 2 | 0 | |
| DBRX | 16 | 4 | 0 | |
| Grok | 8 | 2 | 0 | |
| DeepSeek v1 | 64 | 6 | 2 | 1/4 |
| Qwen 1.5 | 60 | 4 | 4 | 1/8 |
| DeepSeek v3 | 256 | 8 | 1 | 1/14 |
| OlMoE | 64 | 8 | 0 | 1/8 |
| MiniMax | 32 | 2 | 0 | ~1/4 |