| GPU Model | Release Year | NetBW (GB/s) | Compute (FP16 GFLOP/s) | MemBW (GB/s) | Ratio (FLOP/B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V100 | 2017 | 300 | 125,000 | 900 | 139 |
SM version
| 架构 | GPU 型号 | compute capability | nvcc 选项 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volta | V100 | 7.0 | sm_70 |
| Turing | T4, RTX 2080Ti | 7.5 | sm_75 |
| Ampere | A100, RTX 3090 | 8.0 | sm_80 |
| Ampere (Ada Lovelace) | RTX 4090 | 8.9 | sm_89 |
| Hopper | H100, H200 | 9.0 | sm_90 |
Flynn taxonomy
Computer architecture:
- SISD: single instruction stream operates on single data element
- SIMD: single instruction stream operates on multiple
data elements
- Array processor
- Vector processor
SIMD Processing
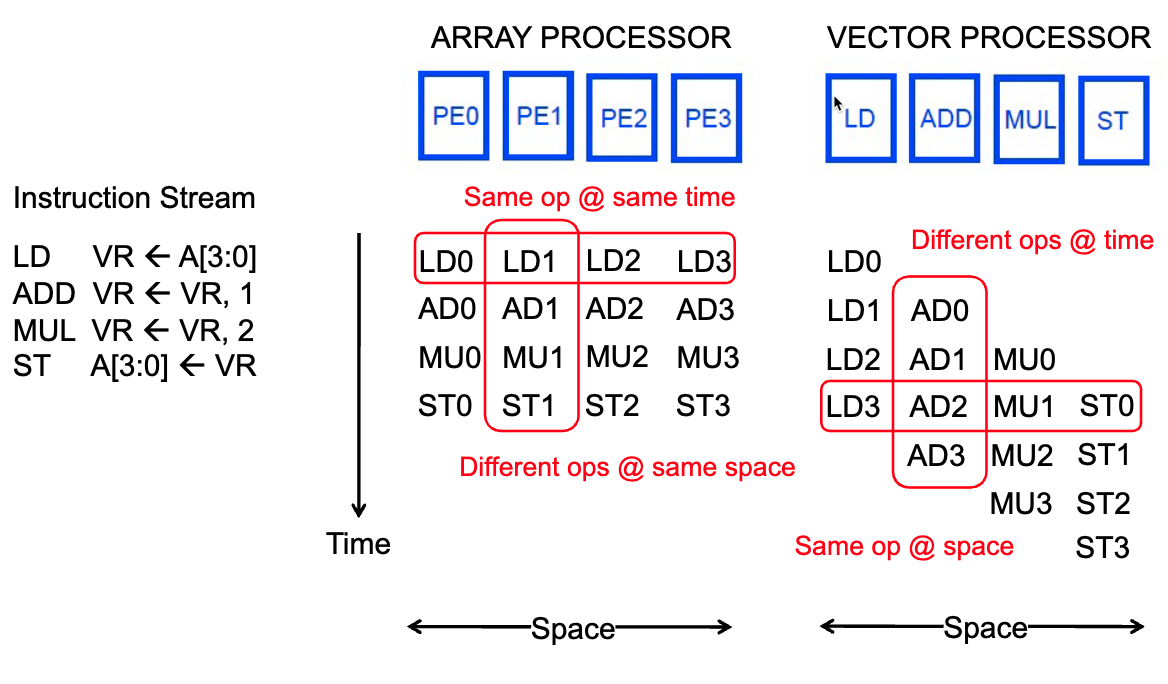
SIMD: in time or in space
Time-space duality
- array processor: Instruction operates on multiple data elements at the same time using different spaces (PEs)
- vector processor: Instruction operates on multiple data elments in consecutive time steps using the same space (PE)
Kernel
CUDA core three key abstractions:
- a hierarchy of threaded groups
- shared memories
- barrier synchronization
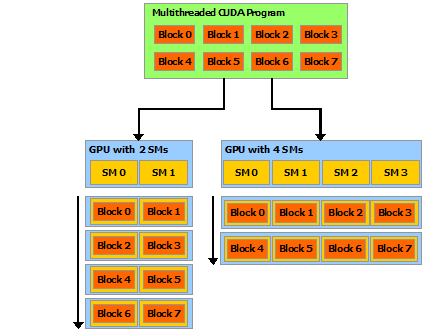
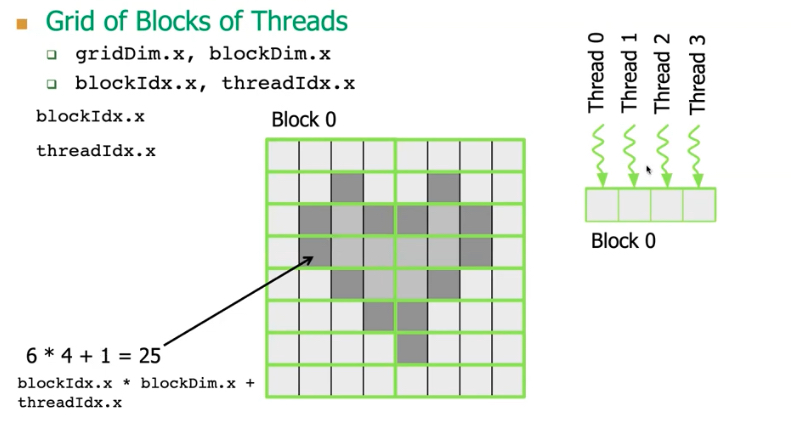
Grid → Block → Warp → Thread
SM (streaming multiprocessor) contains many cores. Each core execute instruction through SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) way, which means it applies the same intruction on multiple data elements at the same time.
Each SM can contain 32-64-128 cuda cores according to the architecture.
Each core can execute multiple warps at the same time. But each thread in these warps must execute the same instruction.
Thread Hierarchy
- kernels: cpp functions executed in
parallel
- defined in
__global__declaration specifier - use
<<<...>>>to specify number of CUDA threads used
- defined in
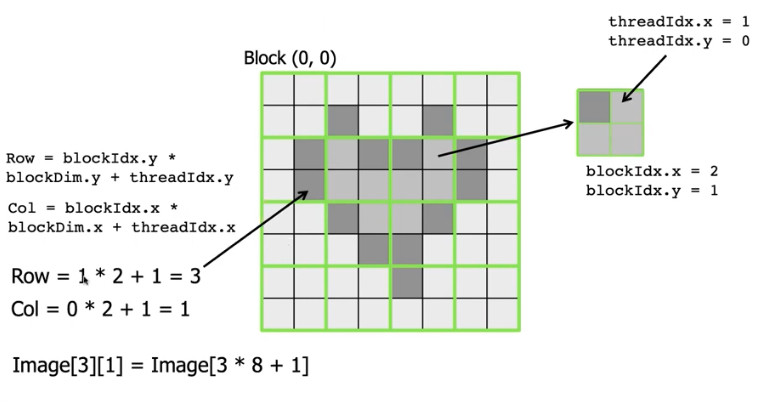
Each block can hold n-dimensional threads. All threads in the same block reside on the same streaming multiprocessor (SM) core and share the limited resource of that core.
Blocks are organized into n-dimensional grid of thread blocks. The number of thread blocks in a grid is usually dictated by the size of the data being processed.
Threads within a block can cooperate by sharing data through some shared memory and by synchronizing their execution to coordinate memory accesses.
Memory Hierarchy
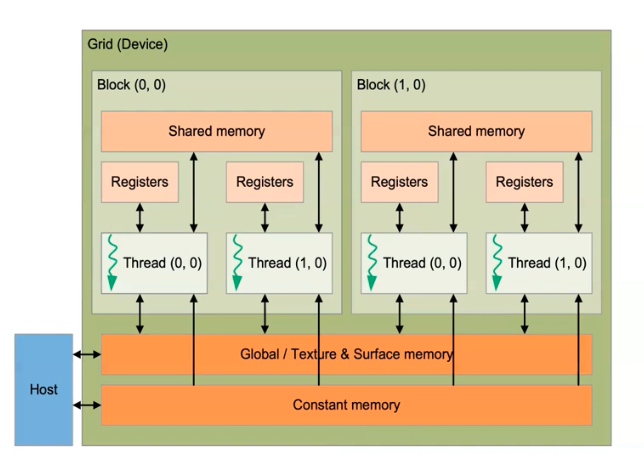
- local memory
- shared memory
- global memory
- texture memory or constant memory: special memory types in the GPU optimized for accessing specific data types such as textures or constant values.
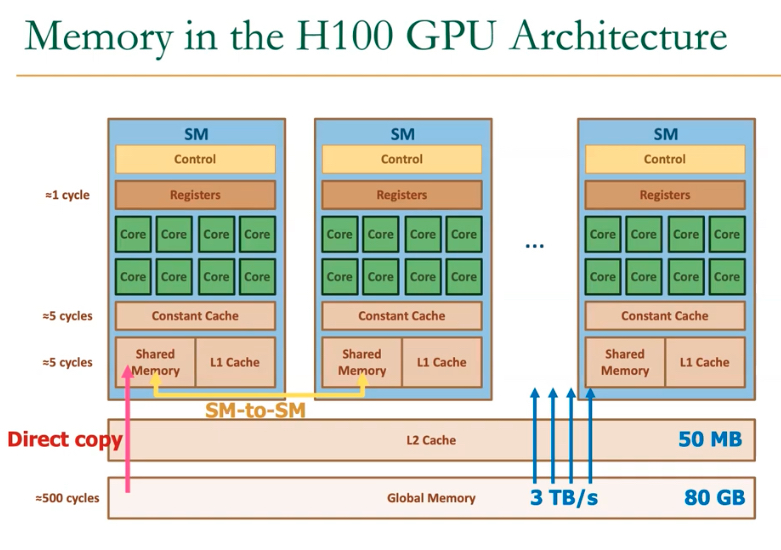
Each SM possesses its own dedicated shared, cache, constant, and register memory. However, multiple SMs share the same global memory.
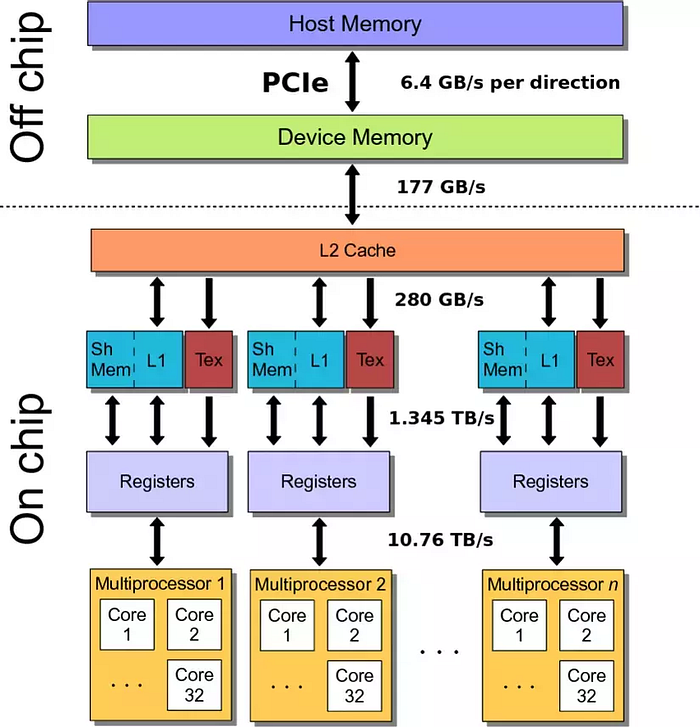
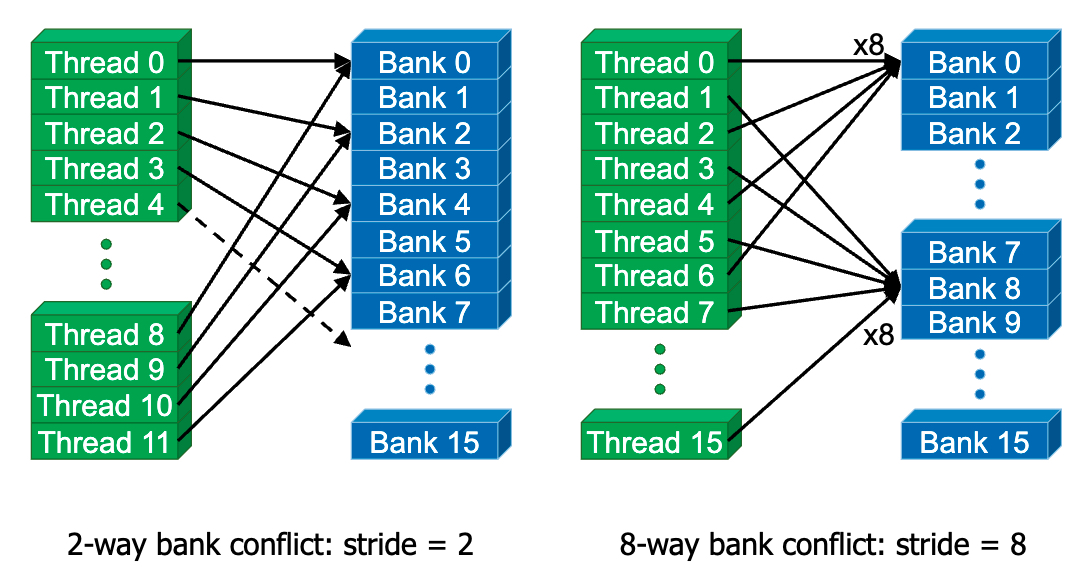
The entire memory is divided into different banks that can be accessed simultaneously. Banks share address and data buses (to minimize pin cost)
Can start and complete one bank access per cycle. Can sustain N concurrent accesses if all N go to different banks.
Traditional Program Structure
Function prototype
float serialFunction(...)
__global__ void kernel(...)
main()
- Allocate memory space on the device:
cudaMalloc(&d_in, bytes) - Transfer data from host to device:
cudaMemCpy(d_in, h_in, ...) - Execution configuration setup: #blocks and #threads
- Kernel call:
kernel<<execution configuration>>(args...) - Transfer results from device to host:
cudaMemCpy(h_out, d_out, ...)
kernel
- automatic variables transparenly assigned to registers
- shared memory:
__shared__ - intra-block synchronization:
__syncthreads()
constant memory
- the mask is small
- it is constant
- it is accessed by all threads
Constant memory is cached inside each GPU core and it is particularly fast when all threads of a warp access the same value
// Declare the mask as a global variable
#define MASK_WIDTH 5
__constant__ float M[MASK_WIDTH];
// Initialize the mask from the host
cudaMemcpyToSymbol(M, M_h, Mask_Width * sizeof(float));Variable Type Qualifier
| Variable declaration | Memory | Scope | Lifetime |
|---|---|---|---|
int LocalVar |
register | thread | thread |
int localArr[N] |
global | thread | thread |
__device__ __shared__ int SharedVar |
shared | block | block |
__device__ |
global | grid | application |
__device__ __constant__ |
constant | grid | application |
__device__ is optional when used with
__shared__ and
__constant__
Performance Consideration
- main bottlenetcks
- cpu-gpu data transfer
- global memory access
- memory access
- latency hiding
- occupancy
- memory coalescing
- data reuse
- shared memory usage
- latency hiding
- SIMD (Warp) Ultilization: Divergence
- Other Considerations
- Atomic opeartions: Serialization
- Data transfers between CPU and GPU
- Overlap of communication and computation
typically, 32 banks in nvidia gpus, bank = address % 32